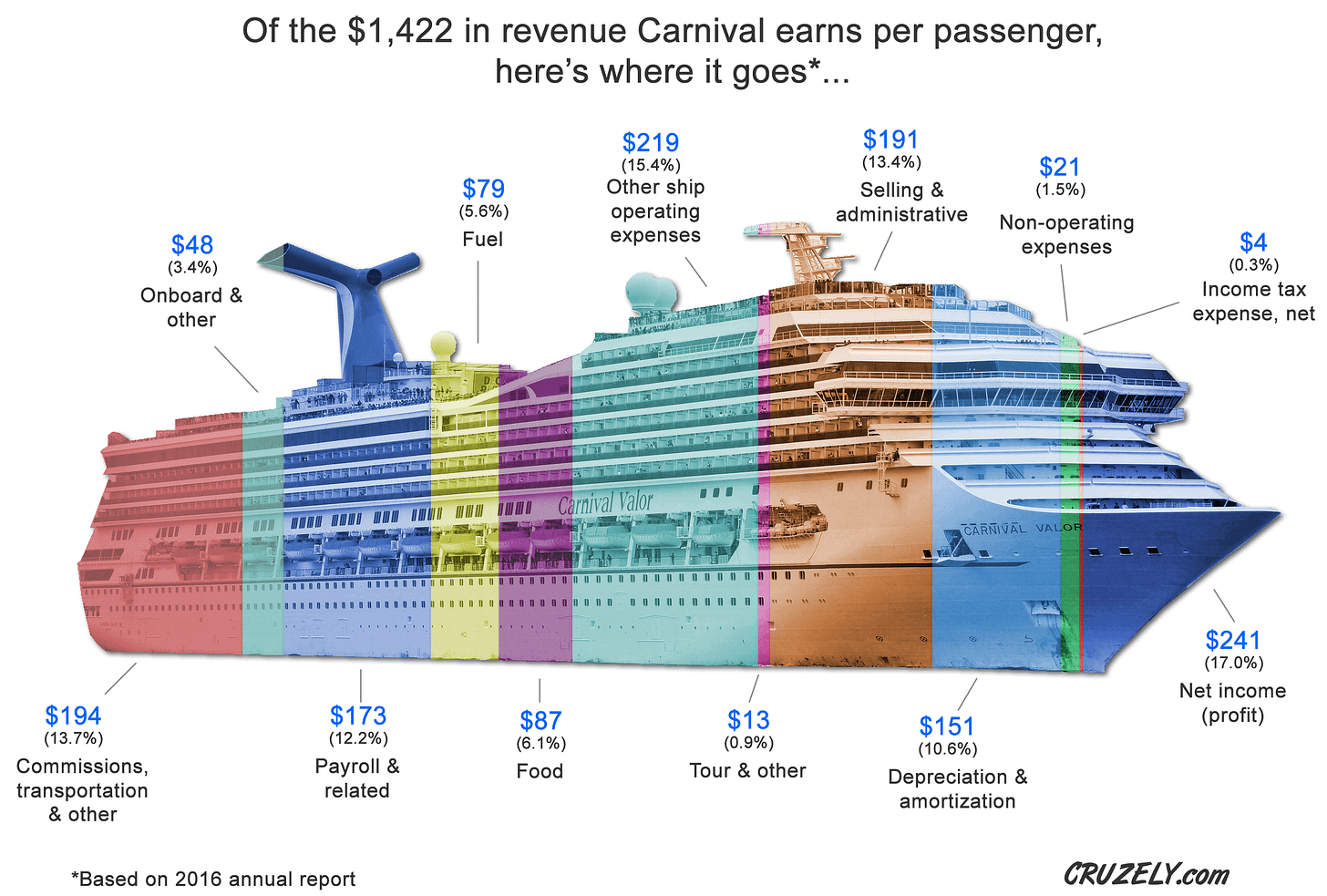
The Business of Cruise Lines: A Look at Revenue and Efficiency
How much money do cruise lines make and how do they do it?
Cruise lines are a major player in the travel industry, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year. In 2019, the global cruise market was valued at $45.79 billion and is projected to reach $64.35 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period (2020-2027).
One of the major players in the cruise industry is Carnival Corporation, the world's largest cruise ship operator. In 2019, the company reported revenue of $18.9 billion, with a net income of $2.6 billion. Royal Caribbean Cruises, another industry leader, reported revenue of $8.9 billion in 2019, with a net income of $1.8 billion.
Cruise lines are able to generate such high revenue by efficiently managing their operations and maximizing occupancy on their ships. They do this by offering a variety of itineraries, destinations, and onboard experiences to appeal to different types of travelers. Additionally, they often offer all-inclusive packages that include meals, entertainment, and activities, which can drive up the overall cost of a cruise vacation.
Cruise lines also employ sophisticated pricing strategies to maximize occupancy and revenue. This includes dynamic pricing, where prices can fluctuate based on demand, and yield management, where prices are adjusted based on factors such as the number of cabins available and the time remaining until departure.
Cruise lines also employ efficiency by utilizing advanced technology to optimize operations and reduce costs. For example, they use data analytics to track and analyze customer behavior, allowing them to make informed decisions about pricing, marketing, and onboard experiences. They also use digital platforms to manage reservations and onboard purchases, reducing the need for physical labor and associated costs.
In conclusion, cruise lines are major players in the travel industry, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year. They achieve this by efficiently managing their operations and maximizing occupancy on their ships, utilizing advanced technology to optimize operations and reduce costs, and utilizing sophisticated pricing strategies to maximize revenue.